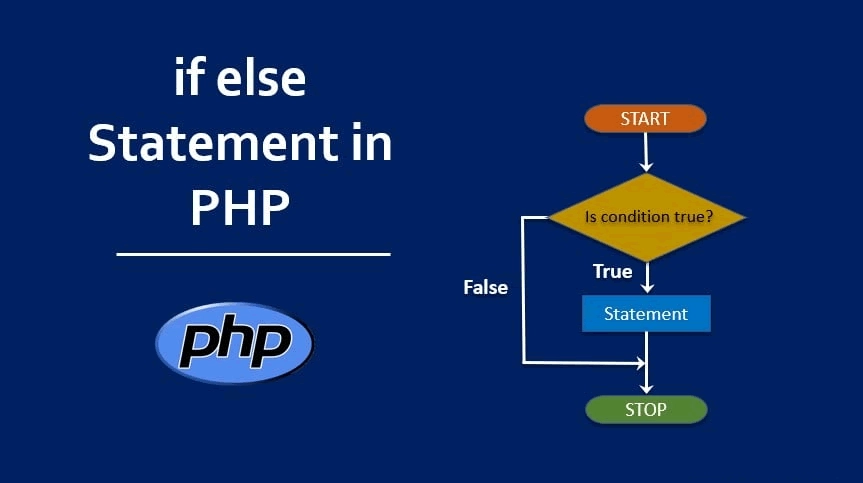
The if else & elseif Statements in PHP
Basic Definitions
Basic if Statement
<?php
$user_age = 20;
if ($user_age >= 18)
{
echo "You are an adult.";
}
?>
The code checks if the $user_age variable is 18 or more. If true, it prints the message. The condition uses the >= comparison operator. Only one statement executes when the condition is met.
Basic if-else Statement
<?php
$current_temperature = 15;
if ($current_temperature > 20)
{
echo "It's hot outside.";
}
else
{
echo "It's not too hot.";
}
?>
The code checks if the current temperature exceeds 15 degrees. If not, the else block executes. This provides a default action when the condition fails. Only one of the two blocks will ever execute.
Multiple elseif Statements
<?php
declare(strict_types=1);
$grade = 85;
if ($grade >= 90)
{
echo "Grade: A";
}
elseif ($grade >= 80)
{
echo "Grade: B";
}
elseif ($grade >= 70)
{
echo "Grade: C";
}
else
{
echo "Grade: F";
}
?>
The code checks the grade against multiple thresholds. It stops at the first true condition. The else provides a default for grades below 70. This pattern is common for grading systems.
Nested if Statements
<?php
declare(strict_types=1);
$user_age = 25;
$user_has_license = true;
if ($user_age >= 18)
{
if ($user_has_license)
{
echo "You can drive.";
}
else
{
echo "You need a license.";
}
}
else
{
echo "You're too young to drive.";
}
?>
The outer if checks user age, while the inner one checks user license status. This creates a hierarchical decision structure. Each condition must be true for the innermost block to execute.
Logical Operators in Conditions
<?php
declare(strict_types=1);
$isMember = true;
$orderTotal = 120;
if ($isMember && $orderTotal > 100)
{
echo "You qualify for free shipping!";
}
elseif ($isMember || $orderTotal > 150)
{
echo "You get 10% discount.";
}
else
{
echo "No special offers available.";
}
?>
The code checks combinations of conditions using && (AND) and || (OR). The first condition requires both to be true. The second needs either one true. Logical operators allow complex condition combinations.
Ternary Operator Alternative
<?php
declare(strict_types=1);
$isLoggedIn = true;
$message = $isLoggedIn ? "Welcome back!" : "Please log in.";
echo $message;
?>
The ternary operator evaluates the condition before the ?. If true, it returns the first expression, otherwise the second. This is useful for simple decisions. It's more compact than full if-else blocks.
Checking array Elements
<?php
declare(strict_types=1);
$user = array(
'name' => 'Kenneth Roggers',
'age' => 25,
'active' => true
);
if (!empty($user['name']) && $user['active'])
{
echo "Welcome, {$user['name']}!";
}
elseif (empty($user['name']))
{
echo "Please set your name.";
}
else
{
echo "Account not active.";
}
?>
The code checks multiple array elements in conditions. It first verifies the name exists and account is active. The empty function checks for non-empty values. array conditions work like variable conditions.
Best Practices
Screen Shots
Click on a photo below to scroll through the screen shots of the application!
Submit your Job or Project Today!
We can help you turn your idea into reality, take over your existing project, or extend your current development team.
Submit your idea job or project below and we will follow up with you shortly.
OUR OBJECTIVE
Our objective is to reach a place where our services will be highly regarded by businesses from various industrial domains for building their innovative busines solutions with our cutting-edge technological expertise, interactive designs and uncompromised quality.
OUR MISSION
We aspire to help businesses ranging from startups to enterprises, who reach out to us with their requirements, in achieving great lengths, expanding their reach, upscaling their products, and generate a large user-base with our outstanding and cost-effective services.